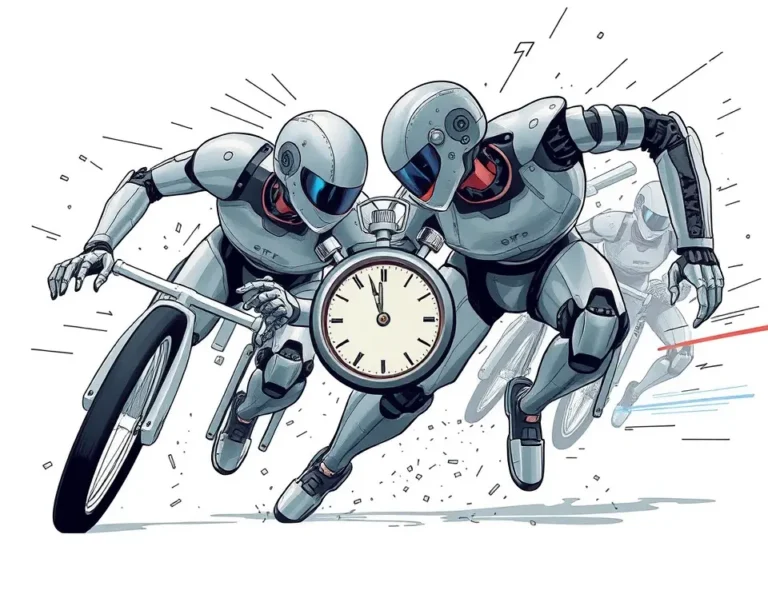
Robots are no longer confined to factory floors or science fiction movies. They’re hitting the pavement, entering the world of competitive running, and quickly closing the gap with their human counterparts. On April 19, 2025, Beijing hosted the world’s first half-marathon featuring both humanoid robots and human runners, marking a historic moment in the fusion of athletic tradition and cutting-edge technology. This event not only showcased the advancements in robotics but also highlighted the challenges and potential of these machines in real-world scenarios.
The Inaugural Robot Half-Marathon
The Yizhuang Half-Marathon in Beijing saw 21 humanoid robots lining up alongside 12,000 human runners. This groundbreaking event was designed to test the endurance, stability, and technological capabilities of these machines in a challenging, real-world environment. While human runners followed conventional rules, the robots competed under tailored guidelines, each supported by a team of human navigators, operators, and engineers. The robots were launched sequentially at intervals exceeding one meter, confined to dedicated tracks where battery swaps mirrored Formula 1’s pit stops.
The Winner: Tien Kung Ultra
The winning robot, Tien Kung Ultra, developed by the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center, completed the 21.0975 km course in 2 hours, 40 minutes, and 42 seconds. Standing approximately 1.8 meters tall and weighing 55 kg, Tien Kung Ultra demonstrated remarkable endurance and navigation capabilities. This victory established a new benchmark for humanoid robot athletic performance and highlighted the potential for these machines to tackle complex terrains and unexpected conditions.
Challenges and Setbacks
Despite the success of Tien Kung Ultra, the race was not without its challenges. Out of the 21 robots that started the race, only six managed to cross the finish line. Some robots fell at the starting line, while others suffered component failures, overheating, or collisions with railings. These setbacks underscored the significant hurdles that still need to be overcome in achieving stable, long-distance running for humanoid robots.
One small robot developed by Beijing Polytechnic University students overheated and went up in smoke. Some other teams sprayed water on their robots to keep them cool. A female-looking robot walked a short distance and fell.
Awards and Recognition
Awards were distributed not just for speed, but for categories like Best Endurance, Best Gait Design, and Most Innovative Form – celebrating both athletic performance and engineering ability.
The Technology Behind the Robot Runners
Creating a robot capable of running a half-marathon requires advanced technology in several key areas:
High-Energy-Density Integrated Joints
Humanoid robots require high-density integrated joints to withstand the stresses of long-duration running. These joints must be compact, lightweight, and capable of generating significant power to propel the robot forward.
Robot Body Heat Dissipation
Heat management is crucial for robots engaged in strenuous activity. Efficient heat dissipation systems are needed to prevent overheating and ensure the reliable operation of the robot’s components.
Robust Motion Control Algorithms
Precise motion control algorithms are essential for maintaining balance, coordinating movements, and adapting to varying terrains. These algorithms must enable the robot to navigate complex environments and avoid obstacles.
Efficient Energy Systems
Long-distance running demands efficient energy systems to maximize battery life and minimize downtime. Robots may utilize battery quick-swap technology or other advanced power management techniques to achieve extended operation.
Wireless Navigation Technology
Unlike typical humanoid robots controlled by remote handles, “Tiangong Ultra” uses wireless navigation technology to follow and plan long-distance paths. It relied on its onboard motion control algorithms and multimodal sensors, combined with ultra-wideband wireless technology to guide the robot in target tracking, calculate its position, and autonomously adjust its running direction and speed in real-time from the start to the finish line.
Software and Hardware Coupling
High coupling between software and hardware was also crucial for long-distance running. Empowered by the general-purpose embodied intelligence platform “Huisi Kaiwu,” “Tiangong Ultra” leveraged the efficient coordination between its “large brain” and “small brain” to show clear advantages in long-distance running.
Comparison with Human Runners
While Tien Kung Ultra’s finishing time of 2 hours, 40 minutes, and 42 seconds is impressive for a robot, it still lags behind the best human runners. The men’s winner of the Yizhuang Half-Marathon completed the course in 1 hour and 2 minutes. The world record for a half-marathon, held by Jacob Kiplimo, is 56 minutes and 42 seconds.
The average half-marathon time for a beginner is between 2 hours and 25 minutes and 3 hours and 15 minutes, depending on age.
Factors Limiting Robot Performance
Several factors contribute to the current performance gap between robots and human runners:
- Energy Efficiency: Human runners are highly efficient at converting energy into motion. Robots, on the other hand, often struggle with energy efficiency, requiring frequent battery changes or pit stops.
- Weight and Size: Human runners are typically lighter and more compact than humanoid robots, giving them an advantage in terms of speed and agility.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Human runners possess remarkable flexibility and adaptability, allowing them to adjust their gait and posture to optimize performance on varying terrains. Robots are still catching up in this area.
- AI and Machine Learning: While AI and machine learning are rapidly advancing, robots still lack the intuitive decision-making capabilities of human runners.
- Durability and Reliability: Human bodies are incredibly resilient and can withstand significant stress. Robots, especially in early stages of development, are prone to mechanical failures and overheating.
Implications for the Robotics Industry
The humanoid robot half-marathon serves as a comprehensive technological validation platform for robots from various companies, not only testing product performance but also demonstrating the potential for industrial-scale applications. The completion of this event further validates humanoid robots’ capabilities in safety, stability, and operational efficiency, promoting applications in more scenarios.
Advancements in AI and Automation
The race highlighted the need for advancements in AI and automation to improve the performance and reliability of humanoid robots. Developing more sophisticated algorithms for motion control, navigation, and decision-making will be crucial for enabling robots to perform complex tasks in real-world environments.
Potential Applications in Various Industries
As humanoid robots become more capable and reliable, they have the potential to revolutionize various industries:
- Manufacturing: Robots can automate repetitive tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce costs in manufacturing processes.
- Healthcare: Robots can assist with surgery, patient care, and medication delivery in healthcare settings.
- Logistics: Robots can automate warehouse operations, package delivery, and transportation logistics.
- Service Industry: Robots can provide customer service, cleaning, and security services in hotels, restaurants, and other public spaces.
- Exploration and Rescue: Robots can be deployed in hazardous environments for exploration, search and rescue, and disaster relief operations.
- Elderly Care: Legged robots to clean the house, do yard work, and even care for the elderly.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the potential benefits of robotics, there are also several challenges and considerations that need to be addressed:
Costs
The high costs of implementation are one of the major challenges when installing industrial robotics. The initial integration process is likely to be long, arduous and expensive. The specifications of new tasks may require redesigning the workspace and repurposing robot workers. Even minor modifications to a manufacturing line may demand a specialist integrator. Smaller-scale SMEs often find the costs unjustifiable or prohibitive.
Job Displacement
Robotic automation could enrich the economy, but that will be at the cost of job loss for at least some humans. This could happen in large numbers and at such a rapid pace, it would be hard for society to adjust.
Ethical Concerns
As robots become more autonomous, ethical concerns arise regarding their decision-making capabilities and potential impact on society. It is important to establish ethical guidelines and regulations to ensure that robots are used responsibly and in a way that benefits humanity.
Workforce Skills
Operators also have to acquire a new level of expertise. Workers don’t usually understand how to operate new types of equipment and, in the case of mobile robots, they don’t know how to behave correctly around them. They often get in the way of a robots path or are confused about the allocation of activities between humans and automated workers. The technology is still relatively new, so there is no embedded academic training as you find with older skills.
The Future of Robot Running
The humanoid robot half-marathon in Beijing marked a significant milestone in the development of robotics and AI. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more impressive feats of athleticism from these machines. In the future, robots may not only compete in races but also assist human athletes with training, provide personalized coaching, and help prevent injuries.
AI-Powered Training
Some running apps and platforms are already using AI to generate training plans, whether you’re aware of it or not. For example, the Runna app, which is a New York Road Runners partner, uses “Runna AI” to continuously adapt a runner’s training plan based on their performance. For example, it may adjust pace target recommendations based on how you’re performing during hard workouts.
Course Intel
AI can provide course previews and information to better dial in your pacing. You could just go to the race’s website, of course, but ChatGPT or other AI tools also aggregate info from multiple sources for you, helping you to get a clearer and more robust picture.
Overcoming Challenges
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing the challenges that currently limit robot performance. This includes improving energy efficiency, reducing weight, enhancing flexibility, and developing more sophisticated AI algorithms. As these challenges are overcome, robots will become more competitive with human runners and capable of performing a wider range of tasks in various industries.
The robots are now coming for your marathon medals.